Express Workflows
What are Express Workflows?
Express Workflows are a new type of AWS Step Functions workflow used to cost-effectively orchestrate AWS compute, database, and messaging services at event rates greater than 100,000 events per second. Express Workflows automatically start in response to events such as HTTP requests via Amazon API Gateway, AWS Lambda requests, AWS IoT Rules Engine actions, and over 100 other AWS and SaaS event sources from Amazon EventBridge. Express Workflows are suitable for high-volume event processing workloads such as IoT data ingestion, streaming data processing and transformation, and high-volume microservices orchestration.
Standard Workflows vs Express Workflows
You can choose Standard Workflows when you need long-running, durable, and auditable workflows, or Express Workflows for high-volume, event processing workloads. Your state machine executions will behave differently, depending on which Type you select. Below is a high-level comparison between Standard and Express Workflows.
| Standard Workflows | Express Workflows: Synchronous and Asynchronous | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum duration | 1 year. | 5 minutes. |
| Supported execution start rate | Over 2,000 per second | Over 100,000 per second |
| Supported state transition rate | Over 4,000 per second per account | Nearly unlimited |
| Pricing | Priced per state transition. A state transition is counted each time a step in your execution is completed. | Priced by the number of executions you run, their duration, and memory consumption. |
| Execution semantics | Exactly-once workflow execution. | Asynchronous Express Workflows: At-least-once workflow execution. Synchronous Express Workflows: At-most-once workflow execution. |
| Service integrations | Supports all service integrations and patterns. | Supports all service integrations. Does not support Job-run (.sync) or Callback (.waitForTaskToken) patterns. |
| Step Functions activities | Supports Step Functions activities. | Does not support Step Functions activities. |
For more information on the differences between Standard and Express workflows, see Standard vs. Express Workflows
Create an AWS Step Functions state machine of type Express from existing Standard state machine
The type of state machine you choose (Standard vs. Express) cannot be changed after your state machine has been created. However, you can create express workflows from existing standard workflows via console by making a copy of the existing state machine and changing the type of the copy.
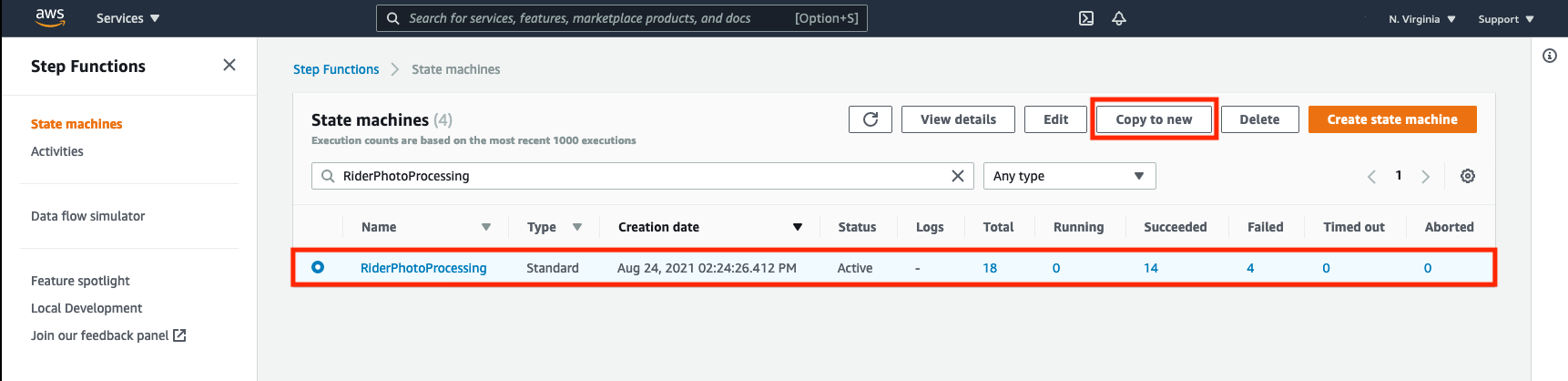
➡️ Step 1: Copy your state machine.
Navigate to the Step Functions dashboard and choose RiderPhotoProcessing state machine and then click on Copy to new.
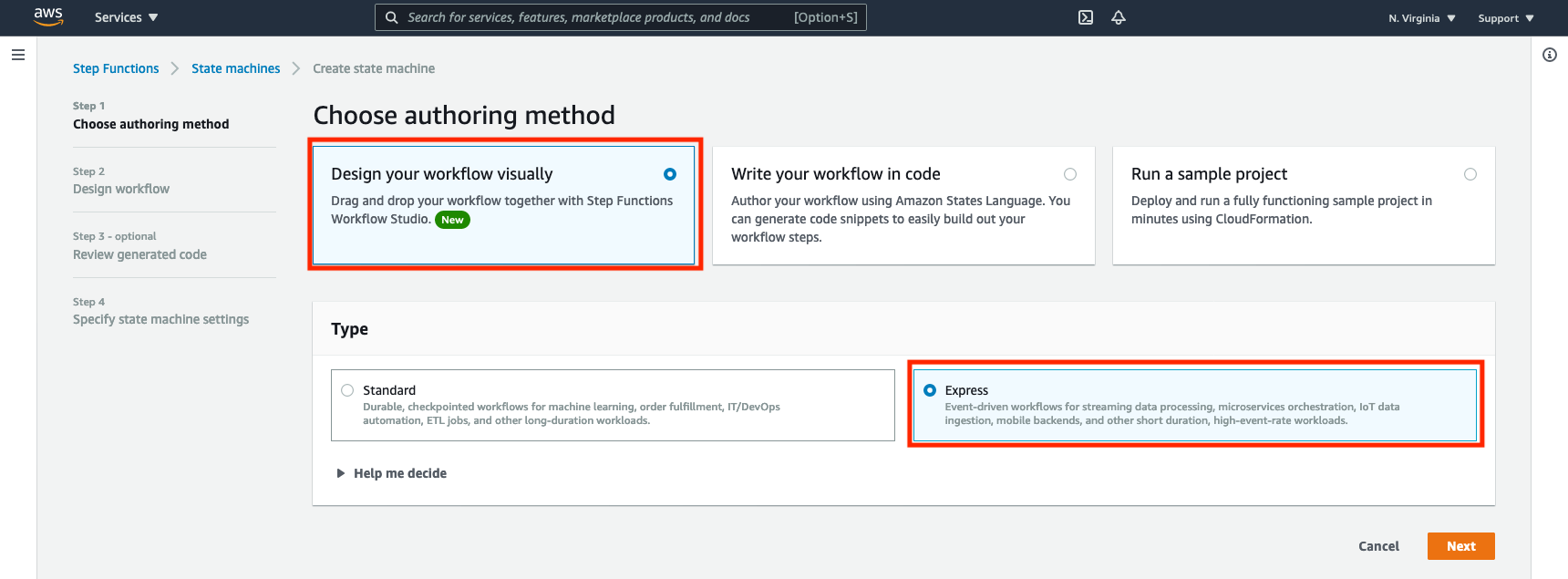
➡️ Step 2: Choose authoring options.
On the Choose authoring method page, choose Design your workflow visually. Then, under Type, choose Express, and then choose Next.
➡️ Step 3: Design the workflow.
On Design workflow don’t change any states. we are going to leave states as is, then choose Next.
➡️ Step 4: Review changes.
On Review generated code - optional choose Next.
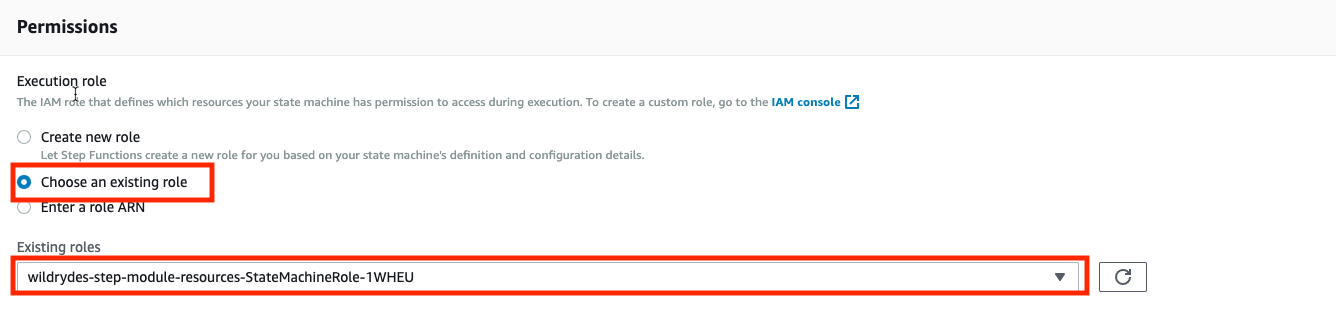
➡️ Step 5: Specify state machine settings.
On Specify state machine settings under Permissions, choose Choose an existing role and choose StateMachineRole from the Existing roles dropdown.
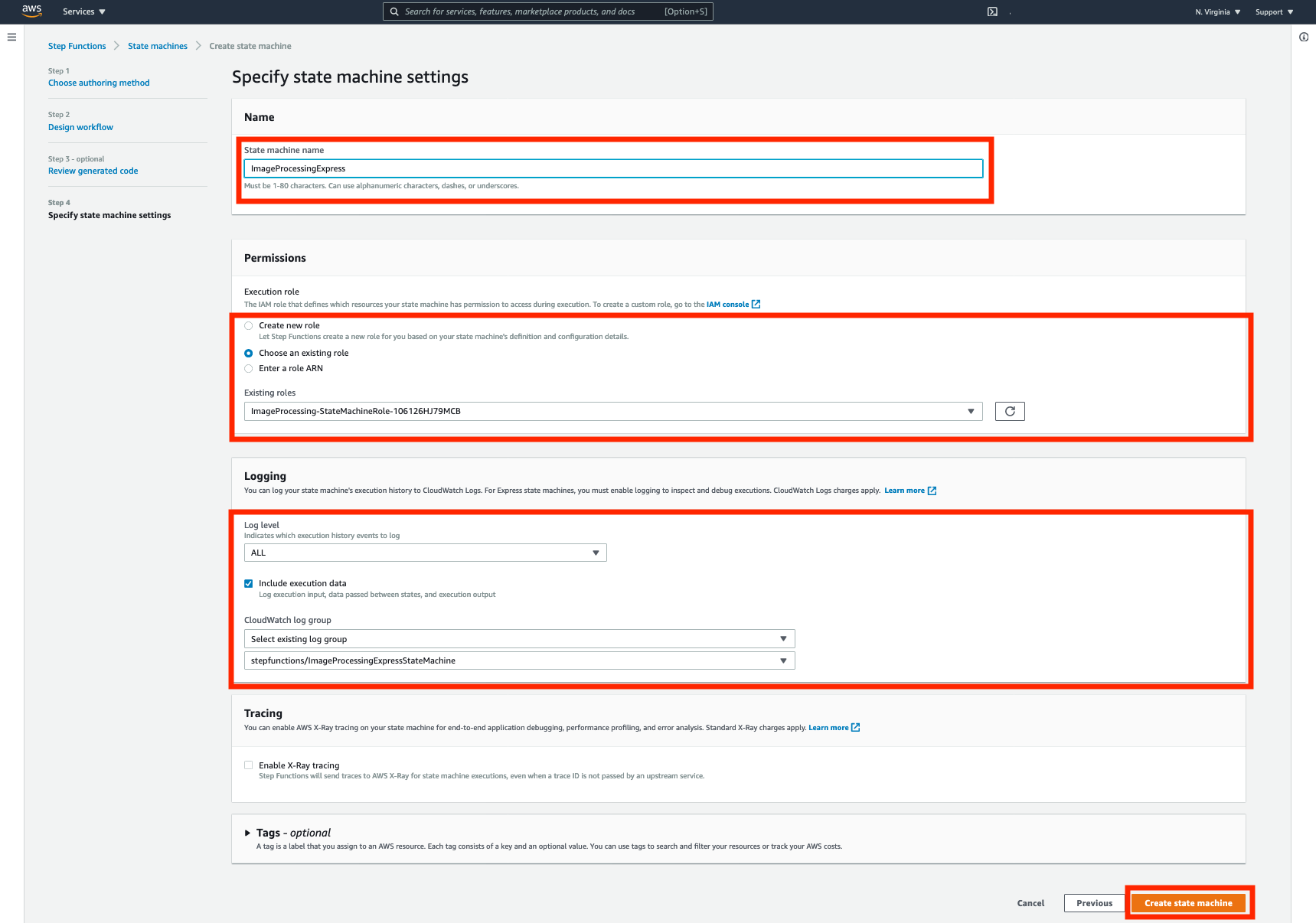
➡️ Step 6: Choose logging options.
In the Logging section, choose the following options:
- For
Log levelchoose ALL from the dropdown. - For
CloudWatch log groupSelect existing log group and choose the existing log group from the CloudWatch log group dropdown (stepfunctions/ImageProcessingExpressStateMachine) created by CloudFormation template.
➡️ Step 7: Press the Create state machine
Testing our implementation
You have created a new express state machine from existing standard ImageProcessing state machine. let’s test our implementation by executing it with some sample input.
Before testing, we need to delete and recreate face collection in Amazon Rekognition.
From this point on, there are two commands to be run from the Cloud9 IDE that will be useful for testing:
Deleting face collection
aws rekognition delete-collection \
--collection-id rider-photos \
--region REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_CHOSEN_AWS_REGION
Creating face collection
aws rekognition create-collection \
--collection-id rider-photos \
--region REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_CHOSEN_AWS_REGION
➡️ Step 8: Return to the AWS Console where you left off, you can click the Start execution button in the top left of the screen.
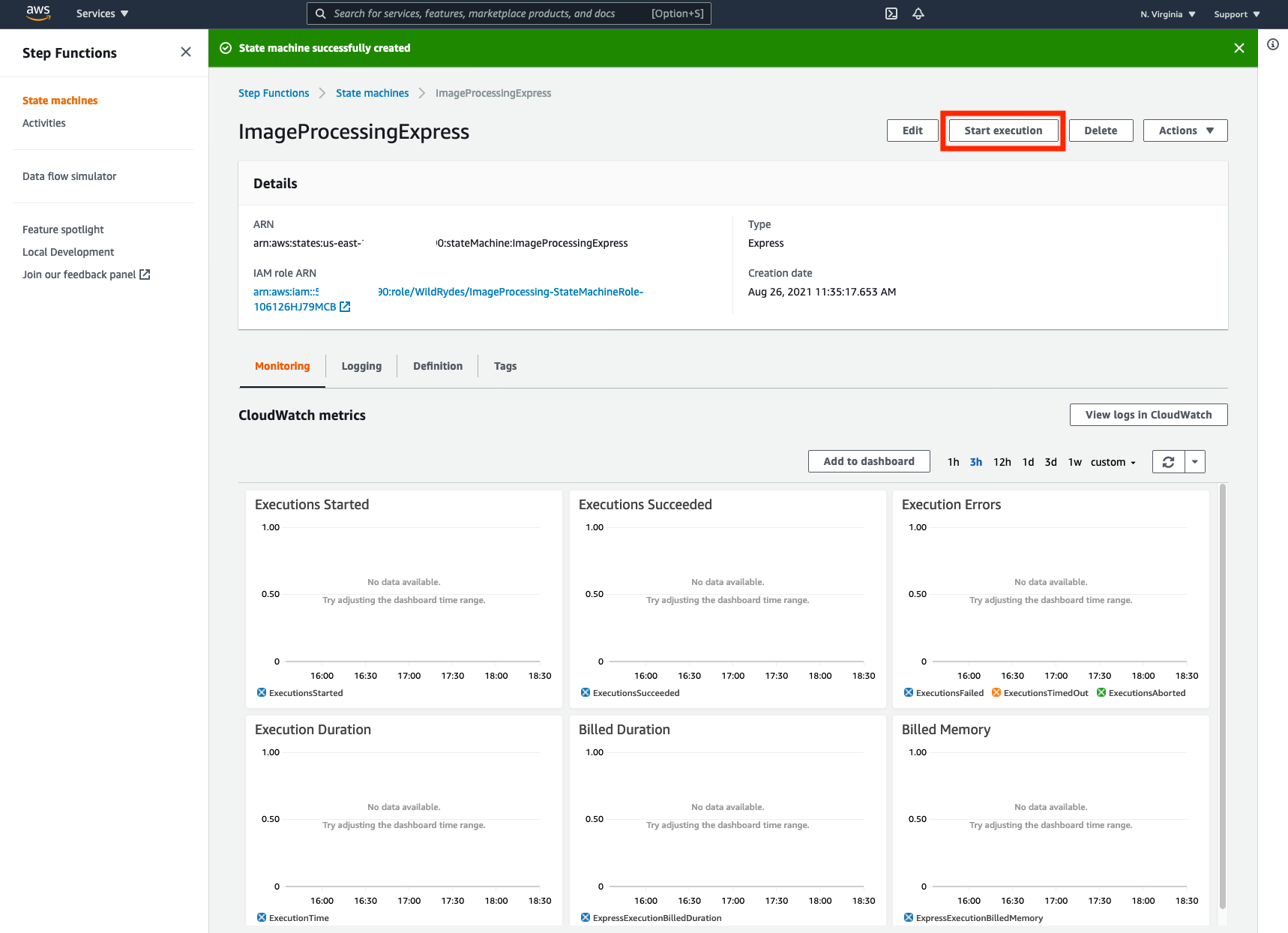
For the input data, copy in the following JSON.
Make sure to substitute the REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_BUCKET_NAME with the value of the RiderPhotoS3Bucket value of the output from the CloudFormation stack.
{
"userId": "user_a",
"s3Bucket": "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_BUCKET_NAME",
"s3Key": "1_happy_face.jpg"
}
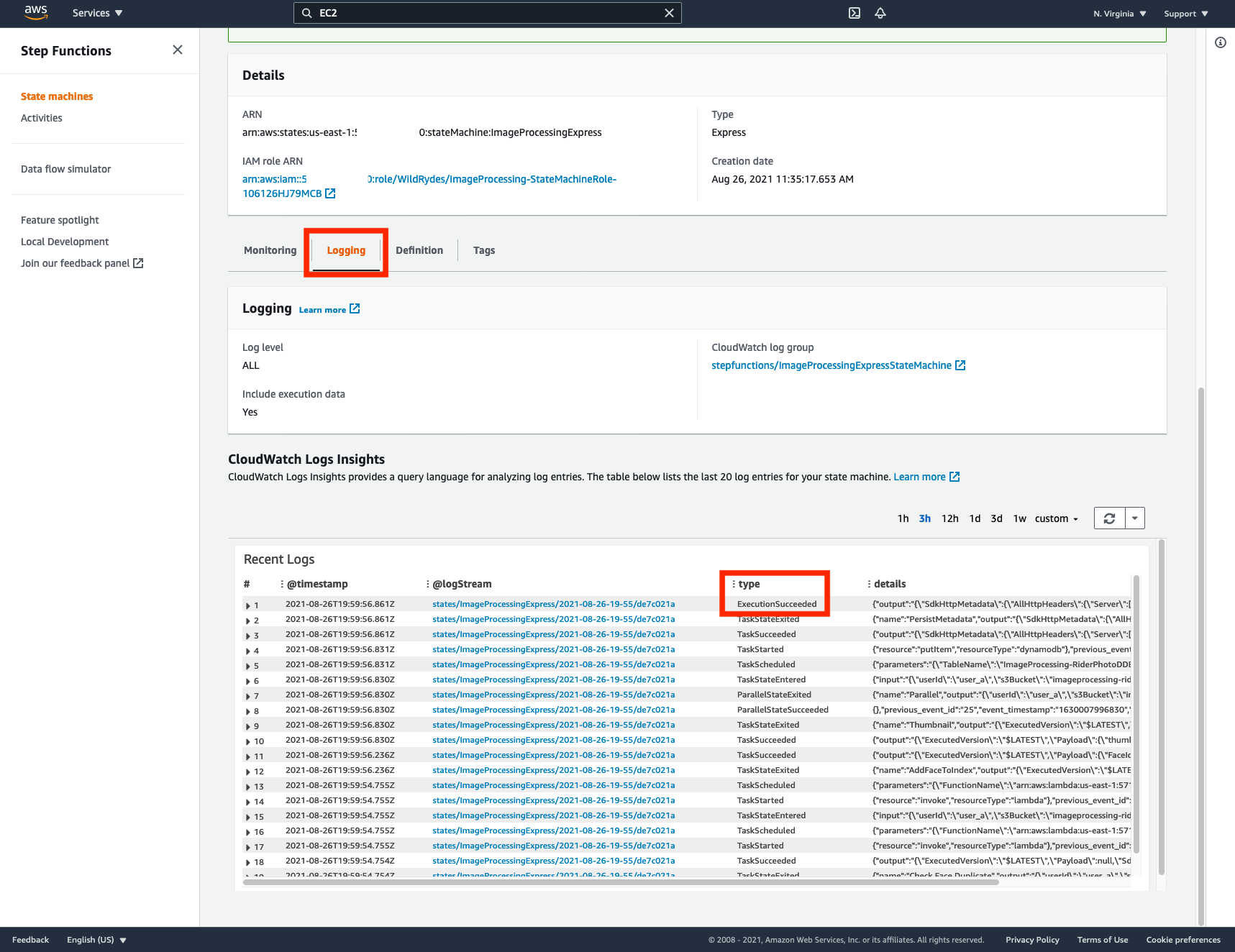
Once you Start Execution, Unlike Standard Woflows, you would NOT see execution results in the visual format as below on the Step Functions Page. This is to get improved performance with Express Workflows. Instead, you have to go to CloudWatch to check the execution status and logs for Express Workflows.
➡️ Step 9: Click on Logging tabs to look in the logs for ExecutionSucceeded.
If the last step succeeds, you can use the AWS CLI to check the list of faces indexed in your Rekognition collection (replace the REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_CHOSEN_AWS_REGION portion with the region string of your chosen region):
Listing face collection
aws rekognition list-faces \
--collection-id rider-photos \
--region REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_CHOSEN_AWS_REGION
Deleting face collection
aws rekognition delete-faces \
--collection-id rider-photos \
--face-ids REPLACE_WITH_ID_OF_FACE_TO_DELETE \
--region REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_CHOSEN_AWS_REGION
You can also use the Amazon S3 Console to check the Amazon S3 bucket created by AWS CloudFormation to store the resized thumbnail images. You should find resized thumbnail images in the bucket.
The name of the S3 bucket can be found in the in AWS CloudFormation output ThumbnailS3Bucket. You can also simply search for it in the S3 Console for wildrydes-step-module-resources-thumbnails3bucket
Troubleshooting Failed Executions
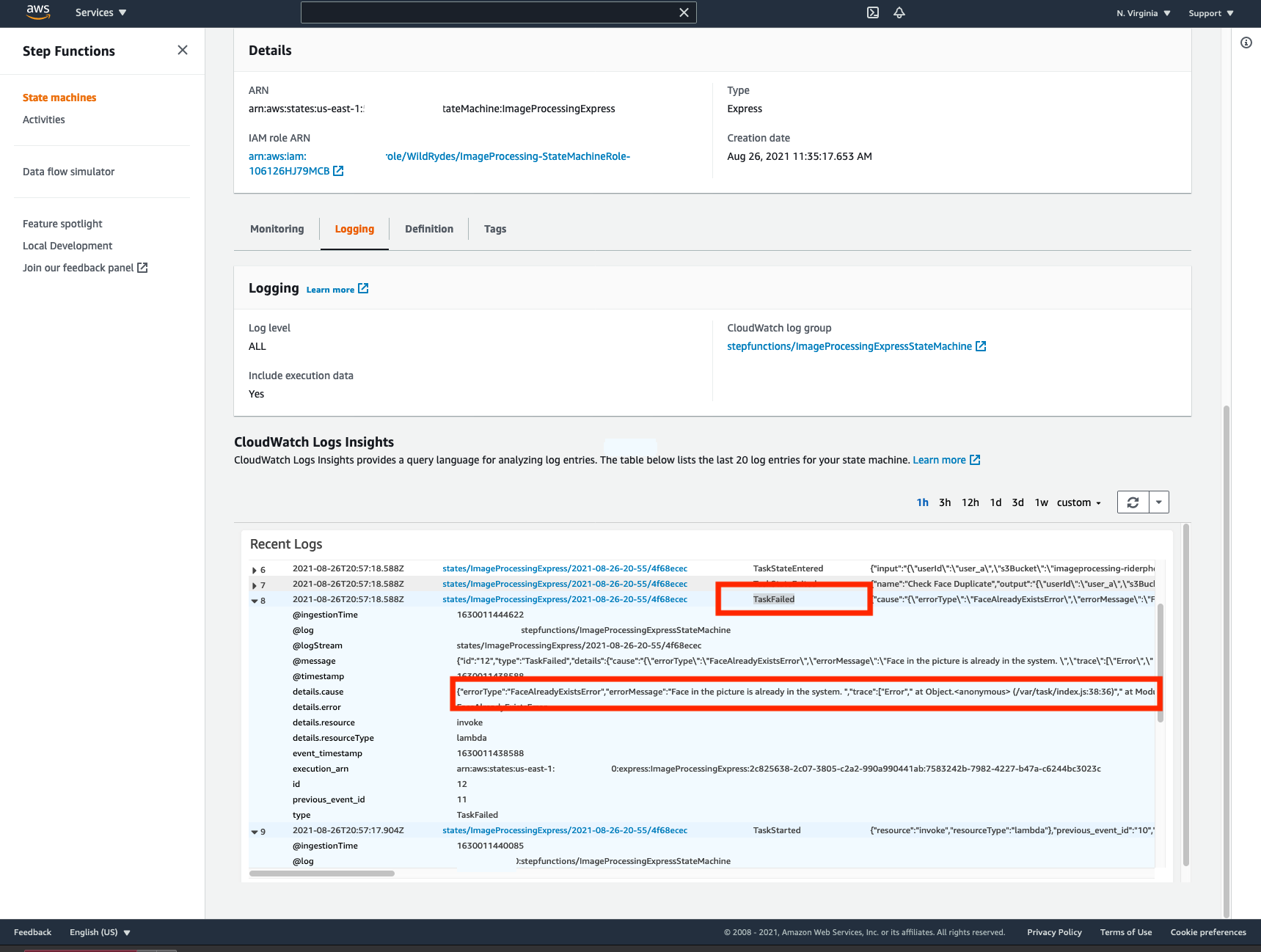
Re-try another execution by passing same input json as before and confirm from the CloudWatch logs that the execution is TaskFailed this time because of FaceAlreadyExistsError error.
✅ Congratulations! You have created and tested Express Workflows state machine.